Instruction Sheet Number 0098-1679: A Comprehensive Overview
Instruction Sheet 0098-1679 details KNX dimmer controllers, Orbit Bot integration, paraffin applications, and embedded systems—a vital resource for comprehensive operational guidance․
Instruction Sheet 0098-1679 serves as a foundational document for understanding and utilizing a diverse range of interconnected technologies․ This comprehensive guide details the functionality of KNX dimmer controllers, specifically those capable of managing lamps via 1-10V reactors, alongside the integration of the XIB ET-0098 Orbit Bot interactive robot․
Furthermore, the sheet provides crucial technical data regarding LINPAR 1416-V normal paraffin, covering its applications in chlorination for flame retardancy, its utility as a solvent, and even its potential as lamp fuel․ Finally, it offers an overview of the embedded controller aspects, including data sheet information and system software considerations․
This document is designed for technicians, installers, and engineers requiring detailed information for proper implementation and troubleshooting․ It’s a critical resource for ensuring optimal performance and safety․
Scope and Purpose of the Document
The Instruction Sheet 0098-1679 encompasses the complete operational spectrum of several integrated systems․ Its primary purpose is to furnish detailed guidance on the installation, configuration, and troubleshooting of KNX dimmer controllers, including 4-channel dimming and 16A switching contacts․
The scope extends to the XIB ET-0098 Orbit Bot, detailing battery installation, Bluetooth pairing, and app functionality․ It also clarifies the technical specifications and safe handling procedures for LINPAR 1416-V paraffin, covering its use as a solvent and in flame retardants․
Ultimately, this document aims to empower users with the knowledge necessary for effective system integration, ensuring adherence to safety guidelines and maximizing performance across all covered components․

Device Functionality & Core Components
Instruction Sheet 0098-1679 covers KNX dimmers, 1-10V reactors, 4-channel control, 16A switching, and the interactive Orbit Bot’s diverse features․
KNX Dimmer Controller Capabilities
Instruction Sheet 0098-1679 details the robust capabilities of the KNX dimmer controller, specifically its ability to manage interfaced lamps via 1-10V reactors․ This controller boasts four independent channels, providing granular control over lighting environments․ Each channel supports dimming functionality, allowing for precise adjustments to light intensity․
Furthermore, the device incorporates four 16A switching contacts, enabling control of standard light loads alongside dimmed circuits․ A key feature is the selectable operational mode – users can choose between normal operation and timer-based control, enhancing flexibility․ Configuration options allow customization of device behavior upon receiving commands, tailoring the system to specific needs․
The BTicino International Product Catalogue highlights this controller as a central component for advanced lighting management systems, offering a blend of dimming and switching capabilities within a KNX framework․
1-10V Reactor Interface Management
Instruction Sheet 0098-1679 emphasizes the critical role of 1-10V reactor interface management within the KNX dimmer controller․ This interface allows for precise control of lamps utilizing 1-10V ballasts or drivers, offering smooth dimming performance․ The controller effectively translates KNX signals into analog 1-10V commands, adjusting lamp output accordingly․
Proper configuration of the 1-10V interface is essential for optimal operation․ The sheet details considerations for reactor compatibility and wiring, ensuring seamless communication․ The system supports a wide range of reactor types, providing flexibility in lighting design․
Effective management of this interface, as outlined in the document, enables energy savings and extended lamp life through controlled dimming․ The BTicino catalogue specifically highlights this functionality as a core benefit of the KNX dimmer controller․
4-Channel Dimming Control
Instruction Sheet 0098-1679 details the robust 4-channel dimming control capabilities of the KNX dimmer controller․ This feature allows independent control of up to four separate lighting circuits, offering versatile lighting scenarios․ Each channel can manage lamps interfaced through 1-10V reactors, providing granular dimming adjustments․
The document outlines how to configure each channel individually, assigning them to specific KNX group addresses for targeted control․ This enables creation of dynamic lighting scenes and personalized user experiences․ The controller supports simultaneous control of all four channels, or independent operation for maximum flexibility․
BTicino’s product catalogue emphasizes this multi-channel functionality as a key advantage, enabling complex lighting designs within a single device․ Proper channel configuration, as detailed in the sheet, is crucial for achieving desired lighting effects․
16A Switching Contacts for Light Loads
Instruction Sheet 0098-1679 highlights the inclusion of four integrated 16A switching contacts, expanding the device’s functionality beyond dimming control․ These contacts provide a convenient method for directly switching standard light loads, such as fluorescent or LED fixtures that don’t require dimming․
The document details how these contacts can be independently controlled via KNX, offering a unified lighting management solution․ Each contact operates as a separate switch, allowing for on/off control of individual lighting circuits․ This feature eliminates the need for additional switching devices, simplifying installation and reducing system complexity․
BTicino’s catalogue emphasizes these contacts as a versatile addition, catering to diverse lighting requirements․ Proper wiring and configuration, as outlined in the instruction sheet, are essential for safe and reliable operation of these switching channels․

Operational Modes & Configuration
Instruction Sheet 0098-1679 details selectable normal or timer modes, alongside command handling configuration, enabling customized behavior upon receiving KNX commands․
Normal Mode vs․ Timer Mode Selection
Instruction Sheet 0098-1679 outlines two primary operational modes for the KNX dimmer controller: Normal Mode and Timer Mode․ Normal Mode functions as a standard dimming system, responding immediately to KNX commands for brightness adjustments․ Conversely, Timer Mode introduces scheduled dimming sequences, allowing pre-defined lighting scenes to activate at specific times․
The selection between these modes is crucial for adapting the system to diverse application requirements․ Normal Mode is ideal for spaces demanding real-time control, such as living rooms or offices․ Timer Mode excels in environments benefiting from automated lighting, like hallways or security areas․ Configuration is achieved through the KNX programming software, enabling users to define the desired mode and associated parameters․
Proper mode selection optimizes energy efficiency and enhances user experience, aligning the lighting system with specific needs and preferences․ The sheet emphasizes careful consideration of the intended application when choosing between Normal and Timer functionalities;
Command Handling Configuration
Instruction Sheet 0098-1679 details extensive command handling configuration options for the KNX dimmer controller․ Users can customize the device’s response to incoming KNX commands, tailoring its behavior to specific application needs․ This includes defining command priorities, filtering unwanted signals, and establishing logical groupings of lights for synchronized control․
The configuration process, managed through KNX programming software, allows for precise control over dimming levels, switching actions, and scene recall․ Users can assign specific KNX group addresses to individual channels or create complex scenarios involving multiple channels․ Furthermore, the sheet highlights the ability to configure the device to acknowledge command receipt, ensuring reliable system operation․
Effective command handling configuration is vital for creating a responsive and intuitive lighting control system, maximizing functionality and user satisfaction․
Behavior Customization Upon Command Reception
Instruction Sheet 0098-1679 emphasizes extensive behavior customization options triggered upon receiving KNX commands․ The controller allows users to define actions beyond simple on/off or dimming adjustments․ This includes setting delays before executing commands, implementing ramp-up or ramp-down sequences for smooth transitions, and establishing conditional responses based on sensor input․
The document details how to configure the device to ignore commands outside a defined time window, preventing unwanted operation during specific hours․ Furthermore, it outlines the ability to set fail-safe behaviors, such as reverting to a pre-defined state in case of communication loss․
These customization features, accessible through KNX programming software, ensure the lighting system operates precisely as intended, enhancing both functionality and user experience․

Technical Specifications & Data
Instruction Sheet 0098-1679 references LINPAR 1416-V paraffin data, chlorination levels for flame retardancy, and embedded controller specifications for detailed technical insight․
LINPAR 1416-V: Normal Paraffin Applications
Instruction Sheet 0098-1679 incorporates data regarding LINPAR 1416-V, a normal paraffin solvent utilized across diverse industrial applications․ Sasol North America’s technical data sheet highlights its versatility․ Specifically, LINPAR 1416-V serves as a direct solvent in numerous processes, demonstrating excellent solvency power for various substances․
Furthermore, it functions effectively as a lamp fuel, showcasing its purity and combustion properties․ The document details its suitability for chlorination, enabling its transformation into valuable flame retardants, plasticizers, and extreme pressure (EP) additives․ This chlorination process achieves high chlorine content, enhancing its performance in these specialized roles․
LINPAR is a registered trademark of Sasol Italy S․p․A․, licensed to Sasol, emphasizing its quality and established industry recognition․ Its consistent composition and reliable performance make it a preferred choice for demanding applications․
Chlorination for Flame Retardancy & Plasticizers
Instruction Sheet 0098-1679 details the crucial role of chlorination in modifying LINPAR 1416-V for specialized applications․ This process elevates the chlorine content to levels ideal for producing effective flame retardants, significantly enhancing material safety by inhibiting combustion․ The resulting chlorinated paraffin compounds are widely used in plastics, textiles, and coatings․
Beyond flame retardancy, chlorination transforms LINPAR 1416-V into valuable plasticizers․ These plasticizers improve the flexibility and workability of polymers, making them suitable for a broader range of products․ They contribute to enhanced durability and performance characteristics․
Additionally, the chlorinated product functions as an extreme pressure (EP) additive in lubricants, reducing friction and wear in demanding mechanical systems․ This versatility underscores the importance of chlorination as a key modification process detailed within the instruction sheet․
LINPAR 1416-V as a Solvent & Lamp Fuel
Instruction Sheet 0098-1679 highlights the diverse applications of LINPAR 1416-V, notably its effectiveness as a solvent in numerous industrial processes․ Its n-paraffin composition provides excellent solvency for various substances, making it suitable for cleaning, degreasing, and extraction procedures․ This characteristic is crucial in formulations requiring a stable and efficient solvent base․
Furthermore, the document details LINPAR 1416-V’s historical and continued use as a lamp fuel․ Its controlled burning properties and relatively clean combustion make it a viable option for specific lamp designs, offering a consistent and reliable light source․
Sasol, the trademark holder, emphasizes the quality and consistency of LINPAR 1416-V, ensuring its suitability for both solvent and fuel applications․ The instruction sheet provides guidance on safe handling and optimal usage for these purposes․

Interactive Robot Integration (XIB ET-0098 Orbit Bot)
Instruction Sheet 0098-1679 covers the XIB ET-0098 Orbit Bot, detailing battery installation, Bluetooth pairing, app downloads, and voice/gesture control features․
Battery Installation Procedures
Instruction Sheet 0098-1679 guides users through the Orbit Bot’s battery installation process, crucial for initial setup and sustained operation․ Begin by locating the battery compartment, typically on the robot’s underside, secured by a small access panel․ Gently release the panel, observing its locking mechanism to avoid damage․
Insert the required batteries – the sheet specifies the type and quantity needed – ensuring correct polarity, as indicated by the + and ‒ markings within the compartment․ Incorrect insertion can prevent operation or damage the robot․ Once batteries are securely in place, carefully reattach the access panel, confirming it clicks firmly shut․
A successful installation is indicated by a power-on light or audible cue․ Refer to the troubleshooting section of Instruction Sheet 0098-1679 if the robot fails to power on after battery installation․
Bluetooth Pairing & Device Connection
Instruction Sheet 0098-1679 details the Orbit Bot’s Bluetooth pairing process, enabling wireless control via a compatible device․ First, ensure Bluetooth is enabled on your smartphone or tablet․ Then, power on the Orbit Bot; it will automatically enter pairing mode, indicated by a flashing LED․
Navigate to your device’s Bluetooth settings and scan for available devices․ The Orbit Bot, identified as “XIB ET-0098 Orbit Bot,” should appear in the list․ Select it to initiate the pairing process․ You may be prompted to enter a pairing code – consult Instruction Sheet 0098-1679 for the default code, if required․
Once paired, the LED will become solid, confirming a successful connection․ Download the ORBIT BOT app (detailed in the sheet) to unlock the full range of control features․ Refer to the troubleshooting section if pairing fails․
Control Interface Description & Navigation
Instruction Sheet 0098-1679 outlines the Orbit Bot’s intuitive control interface, accessible through the dedicated ORBIT BOT app․ The main screen displays a virtual joystick for directional movement – tap and hold to steer․ Below, function buttons control specific actions, such as initiating voice commands or activating gesture recognition․
A settings menu, accessed via the gear icon, allows customization of robot parameters, including speed and sensitivity․ The app’s navigation is designed for ease of use; swipe left or right to cycle through different control modes․ Detailed explanations of each function are provided within the app’s help section, referencing Instruction Sheet 0098-1679 for advanced configurations․
Ensure you familiarize yourself with the interface before operation for optimal control and safety;
Voice and Gesture Control Features
Instruction Sheet 0098-1679 details the XIB ET-0098 Orbit Bot’s advanced voice and gesture control capabilities․ Voice commands, activated by saying “Orbit Bot,” allow hands-free operation – direct the robot with phrases like “Move forward” or “Turn left․” Gesture control utilizes the integrated camera to interpret hand movements; a wave initiates a pre-programmed dance, while a pointing gesture directs the robot’s gaze․
The sensitivity of both systems is adjustable within the ORBIT BOT app, ensuring accurate response in varying environments․ Instruction Sheet 0098-1679 provides a comprehensive list of supported voice commands and gestures․
Troubleshooting tips for recognition issues are also included, emphasizing optimal lighting and clear articulation for best performance․
ORBIT BOT App Download & Functionality
Instruction Sheet 0098-1679 guides users through downloading the ORBIT BOT app, available on both iOS and Android platforms via their respective app stores․ The app serves as the central hub for controlling the XIB ET-0098 Orbit Bot, offering a user-friendly interface for navigation, programming, and customization․
Key functionalities include remote control, scheduled task creation, voice command configuration, and gesture calibration․ Users can define patrol routes, adjust robot speed, and monitor battery levels․ Instruction Sheet 0098-1679 details advanced features like custom gesture programming and integration with other smart home devices․

Regular app updates, detailed within the sheet, deliver new features and performance enhancements․

Embedded Controller Aspects
Instruction Sheet 0098-1679 covers embedded controller data sheets, system software considerations, and appropriate computer classes for optimal controller placement and function․
Embedded Controller Data Sheet Overview
The instruction sheet 0098-1679 references a crucial Embedded Controller Data Sheet, available as a downloadable PDF or text file․ This document provides in-depth technical specifications and operational details regarding the controller’s functionality․ It’s a foundational resource for understanding the system’s architecture and capabilities․
The data sheet outlines the controller’s core components, including processing units, memory configurations, and input/output interfaces․ It details the system software requirements and compatibility considerations, ensuring seamless integration with other devices․ Furthermore, the document explores various classes of computers suitable for hosting the embedded controller, offering guidance on optimal placement and performance․
Users can access this information to troubleshoot potential issues, customize system behavior, and optimize performance․ The sheet also touches upon BIOS updates, highlighting the importance of maintaining current firmware for security and stability․ It’s a comprehensive guide for developers and technicians working with the system․
System Software Considerations
Regarding instruction sheet 0098-1679, robust system software is paramount for optimal device functionality․ The embedded controller relies on specific software configurations to manage KNX dimmer control, 1-10V reactor interfaces, and the Orbit Bot’s interactive features․ Compatibility across different operating systems and hardware platforms must be carefully evaluated․

Software updates are critical for addressing security vulnerabilities and enhancing performance․ Regular updates ensure the system remains stable and responsive․ Developers should consider modular design principles to facilitate future expansions and customizations․ The software architecture must efficiently handle command processing, timer functions, and data communication․
Furthermore, the system software needs to seamlessly integrate with the ORBIT BOT app, enabling voice and gesture control․ Thorough testing and validation are essential to guarantee reliable operation and prevent conflicts․ Proper software documentation is vital for maintenance and troubleshooting․
Classes of Computers & Controller Placement
Considering instruction sheet 0098-1679, the selection of computer classes for system integration depends on processing demands․ Embedded systems, microcontrollers, and potentially single-board computers are suitable, balancing cost and performance․ Controller placement is crucial for optimal signal transmission and accessibility․
For KNX dimmer control and 1-10V reactor management, controllers should be located near the interfaced lamps to minimize wiring complexity and signal loss․ The Orbit Bot’s controller requires strategic placement for effective Bluetooth pairing and voice/gesture recognition․ Centralized control panels offer convenient access for configuration and monitoring․
Network topology impacts controller placement; star, bus, or tree configurations dictate optimal locations․ Environmental factors, such as temperature and humidity, must also be considered․ Secure mounting and protection from physical damage are essential for long-term reliability․
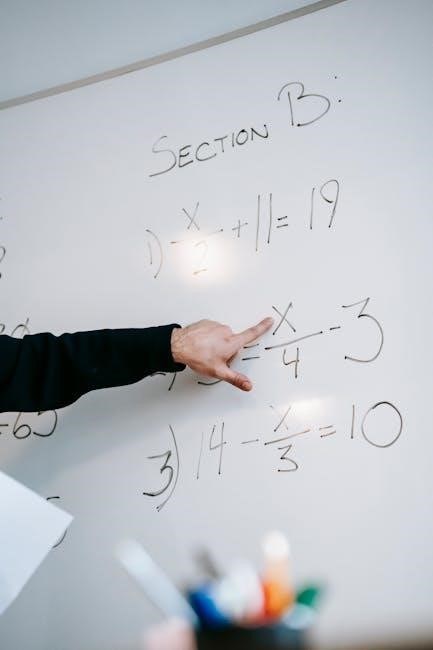
Safety Precautions & Troubleshooting
Instruction Sheet 0098-1679 emphasizes safe installation, proper grounding, and adherence to electrical codes; consult the manual for common issues and solutions․
General Safety Guidelines
Prior to installation and operation, carefully review Instruction Sheet 0098-1679 to understand all safety precautions․ Electrical work should only be performed by qualified personnel adhering to local and national electrical codes․ Always disconnect power before making any connections or adjustments to the KNX dimmer controller, Orbit Bot, or associated systems․
Ensure proper grounding to prevent electrical shock and equipment damage․ Avoid operating devices in excessively humid or wet environments․ Do not attempt to disassemble or modify any component beyond what is explicitly outlined in the documentation․ When handling LINPAR 1416-V, follow the safety data sheet (SDS) guidelines regarding ventilation and personal protective equipment․
Regularly inspect all wiring and connections for damage․ If any issues are detected, immediately discontinue use and consult a qualified technician․ The Orbit Bot’s operational range should be clear of obstructions, and users should be aware of their surroundings during operation․
Common Issues & Solutions
If the KNX dimmer controller fails to respond, verify power supply and KNX bus communication․ For Orbit Bot connectivity problems, ensure Bluetooth is enabled and the device is within range; re-pairing may be necessary․ Issues with LINPAR 1416-V solvent applications should be addressed by reviewing SDS guidelines and ensuring adequate ventilation․
If the embedded controller experiences software glitches, consult the data sheet for troubleshooting steps or consider a system software update․ Dimming inconsistencies may stem from reactor compatibility; confirm proper 1-10V interface management․ Timer mode malfunctions can often be resolved by reconfiguring command handling settings within the controller․
For general operational errors, refer to Instruction Sheet 0098-1679 for detailed diagnostics․ If problems persist, contact technical support with specific error codes and system configurations․
